Overdose Epidemic: Understanding the Crisis and Seeking Solutions
The overdose epidemic is a grave public health concern that has reached alarming proportions. This article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of the overdose epidemic, its causes, effects, and potential solutions. By exploring prevention strategies, treatment options, and support resources, we hope to contribute to the collective effort of combating this crisis.
Understanding the Overdose Epidemic:
The overdose epidemic refers to the sharp increase in drug-related overdose deaths, particularly involving opioids, across communities. It has left devastating consequences in its wake, impacting individuals, families, and communities at large. Key aspects to consider regarding the overdose epidemic include:
Causes of the Overdose Epidemic:
- Prescription opioids: The overprescribing and misuse of prescription opioids have contributed significantly to the epidemic, leading to addiction and subsequent overdose incidents.
- Illicit opioids: The rise of synthetic opioids, such as fentanyl, in the illegal drug market has resulted in an increase in overdose deaths due to their potency and prevalence.
- Lack of awareness and education: Insufficient knowledge about the risks associated with opioid use and the proper management of medications has contributed to the widespread nature of the epidemic.
Effects of the Overdose Epidemic:
- Loss of lives: The overdose epidemic has claimed countless lives, leaving behind devastated families and communities grieving the loss of loved ones.
- Burden on healthcare systems: The surge in overdose cases places a tremendous strain on healthcare systems, including emergency departments and addiction treatment centers.
- Social and economic consequences: The overdose epidemic has far-reaching social and economic impacts, including increased healthcare costs, reduced workforce productivity, and strained social services.
Prevention and Intervention:
- Education and Awareness:
- Public campaigns: Raising awareness about the risks of opioid misuse, proper medication disposal, and the availability of naloxone, an opioid overdose reversal medication.
- Harm Reduction Strategies:
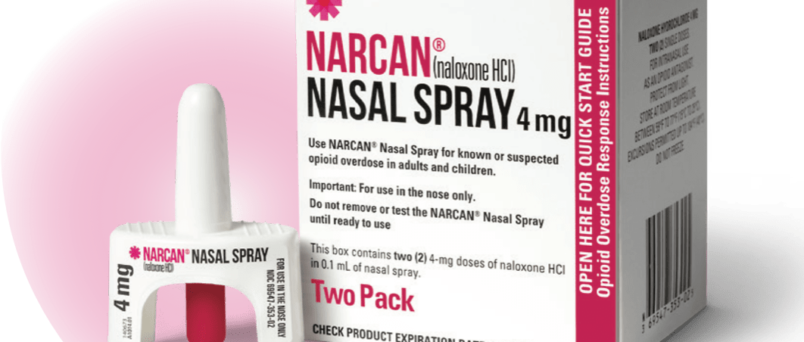
- Access to naloxone: Ensuring that naloxone, a life-saving medication, is widely available to first responders, healthcare professionals, and individuals at risk of overdose.
- Syringe exchange programs: Providing clean needles and harm reduction services to reduce the transmission of infectious diseases among people who inject drugs.
Treatment and Recovery Options:
- Medication-Assisted Treatment (MAT):
- Methadone, buprenorphine, and naltrexone: Medications that can help manage withdrawal symptoms and cravings, while also reducing the risk of overdose.
- Comprehensive Behavioral Therapies:
- Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT): Helps individuals identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors associated with substance use.
- Motivational Interviewing: A collaborative approach that helps individuals explore their motivations for change and build internal motivation for recovery.
FAQs:
Q: How can I prevent an overdose?
A: Understanding the risks associated with opioid use, proper medication management, and accessing naloxone can help prevent an overdose. Seeking help for substance use disorders is also crucial.
Q: Where can I find support for myself or a loved one struggling with addiction?
A: There are various resources available, including addiction helplines, support groups, and addiction treatment centers. Reach out to local healthcare providers or organizations specializing in addiction for assistance.
Q: What should I do if I witness an overdose?
A: Call emergency services immediately. If available, administer naloxone according to instructions or seek help from trained professionals who can administer it.
Discover the path to recovery and get the support you need at More Life Recovery Center.
Call 1 (888) 825-6899
to take the first step towards a healthier, drug-free life.
- National Helpline for Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA): 1-800-662-HELP (4357) Website: https://www.samhsa.gov/find-help/national-helpline
- National Suicide Prevention Lifeline: 1-800-273-TALK (8255) Website: https://suicidepreventionlifeline.org/
- National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA) Helpline: 1-800-662-HELP (4357) Website: https://www.drugabuse.gov/drug-topics/treatment/helpline
- Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) Treatment Locator: Website: https://findtreatment.samhsa.gov/
- American Addiction Centers Helpline: 1-888-685-5770 Website: https://americanaddictioncenters.org/
- Narcotics Anonymous (NA) Helpline: 1-800-622-2255 Website: https://www.na.org/
- Alcoholics Anonymous (AA) Helpline: 1-800-923-8722 Website: https://www.aa.org/
- National Council on Alcoholism and Drug Dependence (NCADD): 1-800-NCA-CALL (622-2255) Website: https://www.ncadd.org/
- Partnership to End Addiction Helpline: 1-855-DRUGFREE (378-4373) Website: https://drugfree.org/
- Overdose Lifeline: 1-800-273-TALK (8255) Website: https://www.overdoselifeline.org/
Please note that some of these resources are helplines that can provide guidance and connect individuals to appropriate services, while others are websites with additional information and resources.